Title: Uniform-Cost Multi-Path Routing for Reconfigurable Data Center Networks
Authors: Jialong Li (Max Planck Institute for Informatics); Haotian Gong (The University of British Columbia); Federico De Marchi (Max Planck Institute for Informatics); Aoyu Gong (École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne); Yiming Lei (Max Planck Institute for Informatics); Wei Bai (NVIDIA); Yiting Xia (Max Planck Institute for Informatics)
Scribe: Gao Han (Xiamen University)
Introduction

The problem studied in this paper is the challenges facing reconfigurable data center networks (RDCNs) in the post-Moore’s Law era. RDCNs are becoming a promising Data Centre Network (DCN) design due to their ability to adapt to different traffic demands by reconfiguring the network topology. However, the dynamic nature of these networks invalidates traditional hop-based routing metrics, resulting in suboptimal performance in terms of latency and bandwidth efficiency. Existing routing solutions struggle to effectively balance these metrics, and a new approach that can cater to the unique characteristics of RDCNs is needed.
Key idea and contribution :
This paper introduces Uniform-Cost Multi-Path routing (UCMP), a new routing method designed for RDCNs. It aims to achieve a balance between low latency and high bandwidth efficiency. UCMP redefines cost metrics by introducing the concept of “uniform cost”, which takes into account the impact of latency and hop count on traffic and balances the importance of these two through a weighting factor.
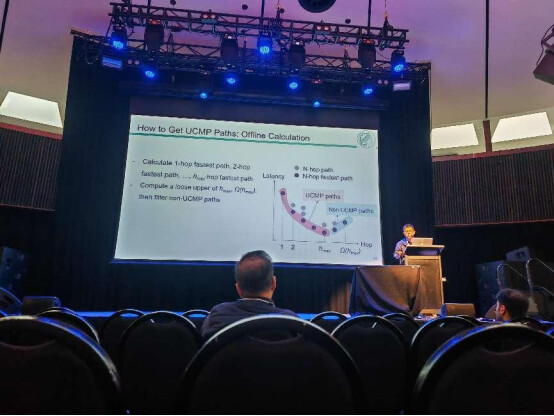
Specifically, offline path computation generates a set of candidate paths that minimize the uniform cost without knowing the traffic size. Online path assignment uses a traffic aging-based traffic bucketing scheme, which allows path assignment without prior knowledge of traffic size and adapts to periodic topology changes in RDCNs. Path selection ensures that the best compromise between latency and hop count is provided by calculating the minimum latency path for each hop. In addition, UCMP allows real-time adjustment of weighting factors based on link utilization to optimize bandwidth efficiency or reduce latency.
UCMP is also designed to be fault-tolerant, providing failure backup paths through multi-path selection to ensure connectivity and stable performance in case of failure.
Evaluation
The evaluation of UCMP is conducted through simulations and testbed experiments, demonstrating its effectiveness against state-of-the-art RDCN routing strategies. The results indicate that UCMP achieves a significant reduction in FCT (53% to 98% lower) and improves bandwidth efficiency by 1.55 times compared to existing solutions. The experimental results demonstrate the potential of the UCMP to significantly improve the performance and efficiency of data center operations.
Q1: You defined hot cards and flow size, but how can latency be considered? Why didn’t you consider bandwidth?
A1: The speaker explained that while they didn’t directly consider bandwidth in the real-time model, the uniform cost model does take bandwidth into account indirectly through an offline model.
Q2: You mentioned adjusting Alpha according to natural capitalization. How do you adjust Alpha online, given the dynamic and bursty nature of traffic?
A2: (The speaker provided an example) In this example, the Alpha is initially set to 1. If the network becomes congested, Alpha is increased to 2. By recalculating the buckets with the new Alpha, the flow maps to different paths, thereby adapting to the network’s dynamic conditions.
Personal thoughts
In this paper, Uniform-Cost Multi-Path (UCMP) is proposed as a natural alternative to ECMP in RDCNs, and simulation results are provided to demonstrate that UCMP reduces traffic completion time and improves bandwidth efficiency compared to previous path selection algorithms. However, the paper could have been more detailed in its explanation of whether UCMP can use arbitrary circuit schedules and the requirements for schedules.